As businesses continue to expand their presence across Southeast Asia, Malaysia stands out as a key destination for talent acquisition and regional growth. In this second part of our Going Global Series, we explore the critical aspects of hiring and compliance in Malaysia, from understanding high-paying roles in the local job market to navigating statutory obligations such as social insurance, the Employees Provident Fund (EPF), and income tax declarations. Whether you’re building your team or ensuring HR compliance, this guide provides practical insights to support your journey into Malaysia’s dynamic employment landscape.
Malaysia: Salary Guide
| Job Title | Job Responsibilities | Average Annual Salary (MYR) | Relevant Degree Requirements |
| Head of banking | Manages bank assets, oversees team operations, ensures budget achievement | 252,000 | Finance, Accounting |
| C-suite roles | Includes CEO, CFO, COO, CIO; responsible for overall company strategy | 400,000 -537,000 | Business Management, Finance, etc. |
| Engineering Director | Leads engineering projects, manages manufacturing and technical teams | 201,480 | Engineering |
| Procurement Director | Oversees corporate procurement, controls cost, optimizes resources | 204,329 | Supply Chain Management, Business Management |
| Finance Director | Manages corporate financial operations, develops financial strategies | 223,080 | Finance, Accounting |
| Managing Director of Operations | Plans corporate operations, enhances efficiency and output | 179,000 | Business Administration |
| Senior Brand Manager (FMGC) | Develops brand strategies, manages marketing campaigns, enhances brand influence, analyzes data, optimizes product positioning and sales | 180,000 – 228,000 | Marketing |
| Senior Business Development Manager | Develops business expansion strategies, identifies market opportunities, drives company growth | 160,000 – 193,000 | Business Administration |
Wage Statistics Data
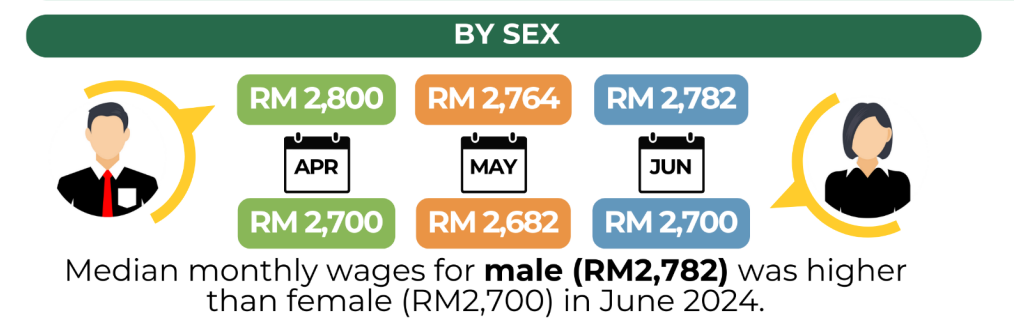
- By Gender: In June 2024, the median monthly salary for males (RM2,782) was higher than for females (RM2,700).
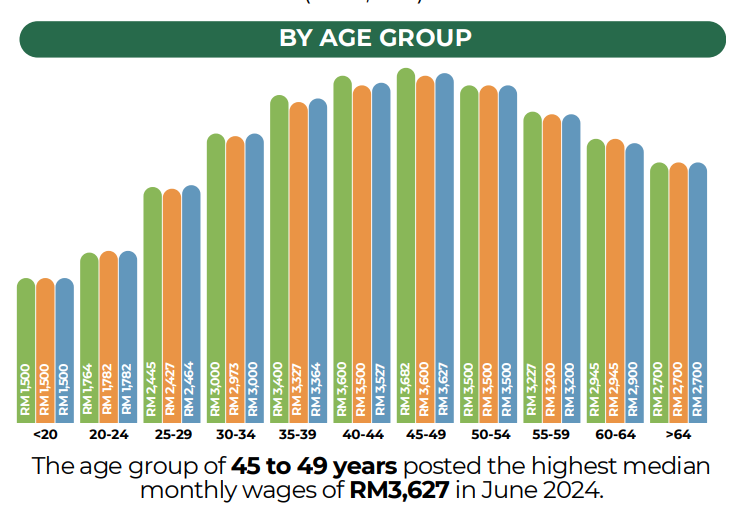
- By Age Group: In June 2024, the highest median monthly salary was recorded in the 45-49 age group at RM3,627.
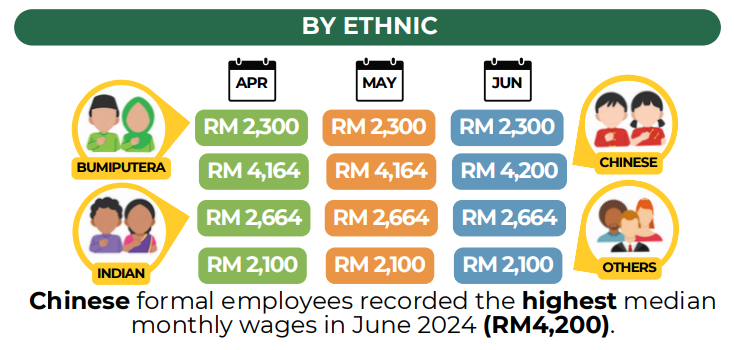
- By Ethnicity: In June 2024, the median monthly salary for formal employees of Chinese ethnicity was the highest at RM4,200.
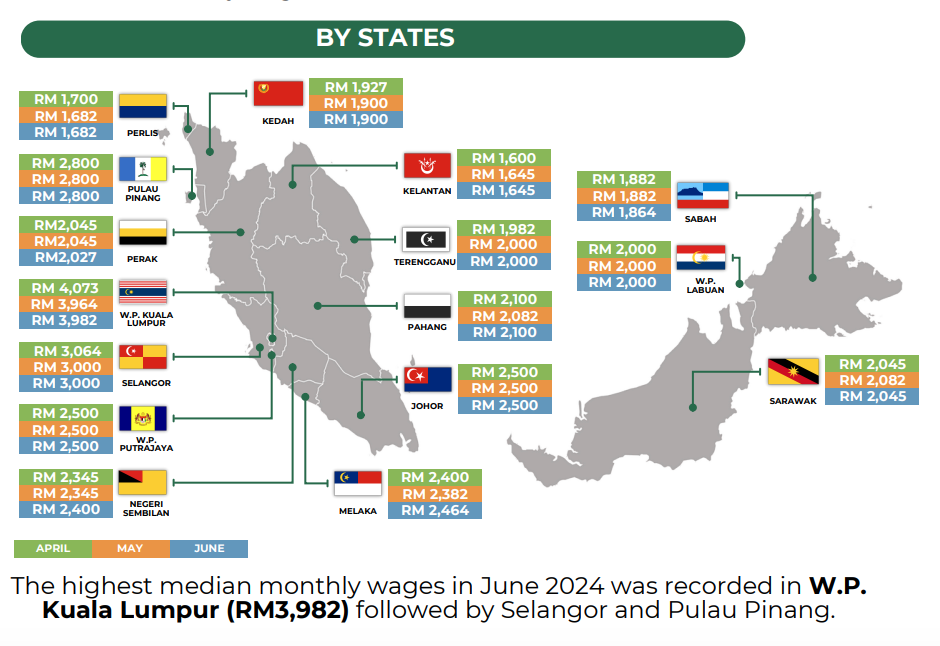
- By State: In June 2024, the Federal Territory of Kuala Lumpur had the highest median monthly salary (RM3,982), followed by Selangor and Penang.
Updated Wage Regulations Effective February 2025
Minimum Wage – Effective February 1, 2025, the minimum wage is set at RM1,700 per month.
Salary Payment – All wages must be paid to employees within 7 days after the end of the pay cycle, including any compensation.
Statutory Social Insurance
| Insurance Type | Purpose |
| Employees Provident Fund (EPF) | Retirement savings scheme |
| Social Security Organisation (SOCSO) | Occupational injury and disability insurance, covering medical expenses, disability benefits, and survivor pensions |
| Employment Insurance System (EIS) | Unemployment assistance, providing short-term financial support and retraining for retrenched employees |
| Human Resources Development Fund (HRDF) | Used for employee training and career development |
Important Notes:
- SOCSO: As of July 2024, foreign employees are required to contribute to SOCSO.
- EIS: Not applicable to foreign employees.
- HRDF: Mandatory for companies with more than 5 employees.
Social Insurance and Employees Provident Fund
| Contribution Type | Employee Contribution | Employer Contribution | Contribution Deadline |
| Employees Provident Fund (EPF)
(No maximum contribution limit) |
11% (Residents under 60 years old) | 13% or 12% (if salary > RM5,000) | 15th of the following month |
| Social Security (SOCSO) | 0.5% (Residents under 60 years old) | 1.75% | 15th of the following month |
| Employment Insurance System (EIS) | 0.2% (Residents aged 18–60) | 0.2% (Residents aged 18–60) | 15th of the following month |
| Human Resources Development Fund (HRDF)
(Only applies to basic salary + fixed allowances) |
N/A | 1% (for 10 or more employees) 0.5% (for 5–9 employees) |
15th of the following month |
How the Employees Provident Fund (EPF) Can Be Used
The Employees Provident Fund (EPF) is a mandatory savings scheme designed to support Malaysians in their retirement. With the 2024 restructuring, EPF savings are now divided into three accounts, each with its own purpose and withdrawal rules.
EPF Account Structure
Account 1 – Retirement Account (75%)
- Holds the largest portion of EPF contributions.
- Purpose: Reserved strictly for retirement.
- Withdrawal: Allowed at age 50, 55, or 60.
Account 2 – Welfare Account (15%)
- Purpose: Can be used for approved purposes related to well-being and development.
- Uses include:
-
- Home purchase
- Medical expenses or equipment
- Higher education tuition fees
- Hajj pilgrimage (for Muslims)
- Purchase of life insurance
Account 3 – Flexible Account (10%)
- Purpose: Allows greater flexibility for contributors.
- Withdrawal: Can be accessed at any time, especially for emergencies or unexpected needs.
📌 When Can EPF Be Withdrawn for Retirement?
- Partial Withdrawal: At age 50 or 55
- Full Withdrawal: At age 60
Employment Insurance System (EIS) Contribution Basis
Income Tax Declaration: TP3 Form Guide
As required by the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (LHDN), all newly hired employees must declare their income from previous employers (within the same assessment year) using the TP3 form to ensure accurate Monthly Tax Deduction (MTD/PCB) calculations.
Who needs to complete the TP3 form?
- New employees who have received income from previous employers within the current year.
- Fresh graduates or employees with no income in the current year (must submit the form with zero income and sign it).
Important Forms Related to Payroll
| Form | Purpose | Submission Deadline |
| Form CP22 | Employers must notify LHDN of new employee onboarding | Within 30 days of joining |
| Annual EA Form | Provided to employees for individual income tax filing | By 28 February each year |
| Annual E Form | Annual report submitted by employers to LHDN (Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia) | By 31 March each year |
2024 Individual Income Tax Rates
For more information, refer to LHDN Tax Rate Guide: https://www.hasil.gov.my/en/individual/individual-life-cycle/how-to-declare-income/tax-rate/
Understanding Malaysia’s talent acquisition landscape and the essential compliance regulations is critical for both employers and employees. As the country continues to grow and evolve, keeping up with these changes will ensure smoother business operations and enhanced workforce management.
In the next part of this series, we will delve deeper into key topics such as annual leave and holiday regulations in Malaysia, the employment of foreign workers, the work visa application process, and the dynamics surrounding blue-collar labour. Stay tuned for Part 3 to gain a comprehensive understanding of these crucial aspects of workforce management in Malaysia.
–
Contact us today!
More information: www.linkcompliance.com
–
Singapore | Malaysia | Indonesia | USA | Japan | China (Shanghai, Beijing, Shenzhen, Hong Kong, Taiwan) | Vietnam | Germany | Turkey | Philippines | United Kingdom | Spain